As the steel with the lowest carbon content in carbon tool steel in DIN 17350 standard,similar to 1045 steel, DIN 1.1730/C45W steel has good strength, toughness and machinability.
After water quenching, DIN 1.1730 steel can obtain good hardness(above 54HRC) and wear resistance, which can be used in hand tools and agricultural implements of all kinds, assembling parts for tools, tongs.
Normally, DIN 1.1730 steel can be delivered without heat treatment, or in an annealed condition(hardness not higher than 190HBW).

DIN 1.1730 STEEL CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S |
| 1.1730/C45W | 0.40-0.50 | 0.15-0.40 | 0.60-0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 |
What is the difference between 1045,C45E and DIN 1.1730 Steel?
First of all, let’s talk about the common points of 1045, C45E and DIN 1.1730 steel, first look at the chemical composition in the table below
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S |
| 1045 | 0.43-0.50 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.05 |
| C45E | 0.42-0.50 | ≤ 0.4 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.035 |
| DIN 1.1730 | 0.40-0.50 | 0.15-0.40 | 0.60-0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 |
We can clearly see that these three steel types are all medium-carbon steels, and the differences in chemical elements are not obvious, which should be said to be negligible.Considering that in some non-important applications, the three can also be used as equivalent steel grades to replace each other.

Let’s talk about the differences. First of all, they come from different standard systems. DIN 1.1730 comes from the German DIN 17350 standard, which belongs to the category of carbon tool steel, while 1045 and C45E come from American ASTM A29 and European EN10083, which belong to the category of carbon engineering structural steel.In addition, in terms of the purity of molten steel, DIN1.1730 and C45E are stricter than 1045.
DIN 1.1730 STEEL FORGING
- Initial Forging Temperature:1180-1210℃
- Final Forging Temperature:>850℃
- Heating Rate:Strictly control the heating speed, which should be uniform and stable to prevent cracking caused by improper heating.Sectional heating is recommended.
- Holding Time:Ensure that the material is fully and evenly heated,and the holding time should not be too long or too short.
- Forging Ratio:above 4:1
- Post-Forging Treatment:According to our experience, DIN 1.1730 steel is generally treated by slow cooling in sand after forged.In addition, softening annealing after forging is also a good choice in advance to prepare for the subsequent process.
DIN 1.1730 STEEL HEAT TREATMENT
- Normalizing:830-880℃,Cool in air.
- Annealing:820-840℃,Cool in furnace,Hardness Max 207 HBW.
- Quenching:800-820℃,Water quench
- Tempering:170-190℃,Harndess >54HRC
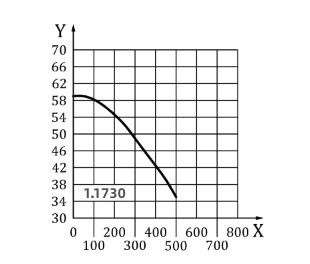
DIN 1.1730 Steel Tempering vs Hardness Diagram
DIN 1.1730 STEEL SUPPLY FORM & SIZE & TOLERANCE
Hot Forged Round bar:Φ80-Φ1000mm
Hot Rolled Round bar:Φ16-Φ350mm
Hot Forged Square bar: Max Thickness:500mm
Flat bar/Blcoks:Thickness :120-800mm ,Width:120-1500mm
| Surface Finish | Black-Forged | Black-Rolled | Rough Turned | Cold Drawn | Peeled | Polished | Grinded |
| Tolerance | 0/+5mm | 0/+1mm | 0/+3mm | Best H11 | Best H9 | Best H9 | Best h8 |
Heat treatment:Quenched and Tempered (+QT), Normalizing (+N), Annealing (+A)
Surface finish:Black / Rough turned / Peeled
















