As the most widely used Cr-Mo series pre-hardened plastic mold steel,P20 steel has good machinability,good polishing and photo-etching properties.Since it has been quenched and tempered, P20 steel can be processed directly without further heat treatment, and the processed material has uniform hardness and good dimensional stability.
Main characteristics of P20 steel
- After vacuum degassing and refining treatment, P20 steel has high purity,and suitable for plastic molds that require polishing or etching.
- Supplied in a pre-hardened(Quenching & Tempering) conditon, P20 steel can be directly used for mold processing without heat treatment, shortening the construction period.
- After forging and rolling, the structure of P20 steel is stable and uniform,100% ultrasonic inspection, no pores, pinhole defects.
- P20 has good machinability and mirror polishability.
P20 Steel Supply Form & Size & Tolerance
| Supply Form | Size(mm) | Process | Tolerance | |
Round | Φ6-Φ100 | Cold Drawn | Bright/Black | Best H11 |
Φ16-Φ350 | Hot Rolled | Black | -0/+1mm | |
| Peeled/ground | Best H11 | |||
Φ90-Φ1000 | Hot Forged | Black | -0/+5mm | |
| Rough Turned | -0/+3mm | |||
Flat/Square/Block | Thickness :120-800 | Hot Forged | Black | -0/+8mm |
| Width:120-1500 | Rough Machined | -0/+3mm | ||
Remark:Tolerance can be customized as per requests
P20 Steel Equivalent Grade Chemical Composition
| Standard | Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo |
| ASTM A681 | P20 | 0.28-0.4 | 0.2-0.8 | 0.6-1.0 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.4-2.0 | 0.3-0.55 |
| DIN ISO 4957 | 1.2311 | 0.35-0.45 | 0.2-0.4 | 1.3-1.6 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.8-2.1 | 0.15-0.25 |
| GB/T 1299 | 3Cr2Mo | 0.28-0.4 | 0.2-0.8 | 0.6-1.0 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.4-2.0 | 0.3-0.55 |
P20 Steel Physical Property
| Temperature | 20°C | 200°C |
| Density,kg/m3 | 7800 | 7750 |
| Modulus of elasticity,N/mm2 | 250000 | 200000 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion,per °C from 20°C | — | 12.7 x 10 ^–6 |
| Thermal conductivity,W/mk | 29 | 29.5 |
| Specific heat,J/kg °C | 460 | — |
P20 Steel Mechanical Property
- P20 Steel Mechanical property in Annealed condition
| Testing temperature | 200°C | 400°C | 500°C |
| Tensile strength Rm,N/mm2 | 860 | 780 | 610 |
| Yield strength Rp 0.2,N/mm2 | 640 | 570 | - |
| Elongation ,% | 17 | 18 | 26 |
| Reduction ,% | 55 | 65 | 70 |
Remark: Annealing temperature:760-790°C
- P20 Steel Mechanical property in Q & T condition
| Testing temperature | 200°C | 400°C | 500°C |
| Tensile strength Rm,N/mm2 | 1000 | 950 | 685 |
| Yield strength Rp 0.2,N/mm2 | 810 | 760 | 350 |
| Elongation ,% | 13 | 17.4 | 23 |
| Reduction ,% | 56.5 | 66 | 88 |
Remark:860°C quenching,650°C tempering
P20 Steel Forging
Heat AISI P20 to the temperature 700 oC ,hold for suitable time,then heat the temperature uniformly to 900 oC – 1100 oC.Forging below 870°C is not recommended for P20. Cooling in sand after forged.
P20 Steel Heat Treatment
- Stress Relieving
After rough machining ,P20 should be heated through to500- 550°C, holding time 2 hours. Cool slowly in the furnace to room temperature.
- Annealing
Heat P20 in a protective atmosphere (preferably a controlled atmosphere furnace) to 720-750°C,and hold for one hour per inch of thickness. Cool in the furnace at 10°Ccper hour to 600°C,Then air-cool to room temperature.The resulting hardness Is Brinell 235 max.
- Quenching & Tempering
Preheating temperature: 500–600°C
Austenitizing temperature: 880°C.
The steel should be heated through to the austenitizing temperature and hold at temperature for 30 minutes. Protect the tool against decarburization and oxidation during the hardening process.
Quenching Media
• High speed gas/circulating atmosphere. (Only suitable for small dimensions)
• Oil (Warm oil (65-80°C))
• Martempering bath 300°C, max. 4 minutes,then air cool
Note: Temper immediately when tool reaches 50–70°C.
Choose the tempering temperature according to the hardness required by reference to the tempering graph. Temper twice with intermediate cooling to room temperature. Lowest tempering temperature 180°Cfor small inserts, but preferred minimum is 250°C, unless material is to be nitride or nitrocarburized later. Holding time at temperature minimum 2 hours.
| Tempering,°C | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 550 | 600 |
| HRC | 56 | 54 | 51 | 47 | 44 | 42 | 39 | 36 |
| Rm,N/mm2 | 2050 | 1910 | 1730 | 1530 | 1400 | 1330 | 1230 | 1140 |
P20 Steel Application
AISI P20 tool steels are used for low temperature applications that include injection molds and die casting dies. Typical application are:
• For large injection and compression molds
• Extrusion dies for thermoplastics
• Blow molds
• High strength holders, plates and bolsters
• Forming tools, press-brake dies (possibly flame hardened or nitrided)
• Aluminum die casting prototype dies
• Zinc die casting dies
• Long run die shoes
• Structural components, shafts
P20/DIN 1.2311 STEEL BUYING GUIDE
As the representative steel grades in plastic mold steels, P20 and 1.2311 steels have a wide range of industrial applications, and this huge demand also leads to uneven levels of quality of these two materials in the market. How to choose high-quality P20 and 1.2311 steel is a difficult problem for consumers.
Therefore,we will do something right and meaningful to help people choose P20 and 1.2311 steel reasonably and efficiently through this guide,and no longer worry about being unable to start.
If you have this need, then start learning from here.

WHAT IS P20/DIN 1.2311 STEEL?
We all know that P20 belongs to the American steel grade, so what does it specifically represent?According to the classification of the Tool Steel Committee of the American Society for Metals, P20 belongs to the plastic mold steel in the three major classifications of tool steel.
The United States is the first country to list special steel for plastic molds in tool steel, mainly represented by the capital letter P.As a medium carbon Cr-Mo series steel, P20 steel belongs to the quenched and tempered plastic mold steel.At present, in the application of plastic molds, P20 steel is used in a large amount as the main steel grade, and it is mostly used in the pre-hardened condition.
For DIN 1.2311 steel,it belongs to the German steel grade. It is named 1.2311 according to the German DIN 17007 numerical steel number system,which is expressed as alloy tool steel. In addition, 1.2311 corresponds to 40CrMnMo7 under the DIN 17006 naming system.
Introduction to Three Types of “P20 Steel” From ASSAB
- ASSAB 518
As a vacuum-degassed Cr-Mo alloy steel,ASSAB 518 is supplied in pre hardened condition with hardness 280-320HB.ASSAB 518 does not require further heat treatment and can be processed directly, which can eliminate the risk of cracking and deformation during heat treatment, reducing processing cycle and cost.
ASSAB 518 Main Characteristics:
- Good homogeneity and uniform hardness
- Good machinability
- Good polishing and photo-etching properties
- Good weldability
- Suitable for all nitriding processes, hard-chromium plating, PVD coating as well as case hardening (carburising)
ASSAB 518 Applications:
- Injection moulds for thermoplastics
- Extrusion dies for thermoplastics
- Blow moulds
- Mould/die frames and holders
- Machine and structural components (e.g. shafts, gears, hammers, etc.)
- ASSAB 618/618HH
ASSAB 618 HH is a pre hardened mould steel with hardness of 340 – 380 HB,which is higher than ASSAB 618 and ASSAB 718 Supreme.The higher hardness gives an increased resistance to wear and indentations,which means enhanced mould life.
ASSAB 618 HH is manufactured to consistently high quality standards with a low sulphur content,which gives this steel with the following characteristics:
- Good polishing and photo-etching properties
- Good machinability
- High purity and good homogeneity
- Uniform hardness
ASSAB 618HH Applications:
- Injection moulds for thermoplastics
- Extrusion dies for thermoplastics
- Blow moulds
- Forming tools, press-brake dies (possibly flame hardened or nitrided)
- Aluminium die casting prototype dies
- Structural components, shafts
- ASSAB 718 Supreme/718HH
ASSAB 718 Supreme/718HH is obtained by further improving the purity of steel on the basis of 618/618HH. It is manufactured to consistently high quality standards with a very low sulphur content(S<0.01%),which gives this steel with the following characteristics:
- Good polishing and photo-etching properties
- Good machinability
- High purity and good homogeneity
- Uniform hardness
ASSAB 718HH Applications:
- Injection moulds for thermoplastics
- Extrusion dies for thermoplastics
- Blow moulds
- Forming tools, press-brake dies (possibly flame hardened or nitrided)
- Aluminium die casting prototype dies
- Structural components, shafts
QUICK FAQS FOR P20/DIN 1.2311 STEEL
What is P20+S,P20+Ni?
On the basis of P20 steel, additional sulfur content is added(S:0.05-0.1%), which is P20+S steel.It improves the machinability of P20 steel.
Similarly, the nickel element is added on the basis of P20 steel(Ni:0.9-1.2%), which is P20+Ni steel.The addition of Ni not only improves the polishing performance, but also has higher pre-hardening hardness.
Is P20 steel corrosion resistant?
Although P20 steel has high hardness, good toughness, and strong tensile strength, it does not belong to the category of stainless steel. It will naturally oxidize and rust in the environment of conductive media such as water and salt, so it does not have strong anti-rust and anti-corrosion properties.
Can P20 Steel be nitrided?
In order to obtain better surface wear resistance and corrosion resistance, P20 steel can be achieved through nitriding treatment.The surface hardness after gas nitriding at 525°C in ammonia gas will be approximately 650 HV with the following case depth.
| Temperature,°C | Time,h | Depth,mm |
| 525 | 20 | 0.3 |
| 525 | 30 | 0.35 |
| 525 | 60 | 0.5 |
What is the hardness of P20 steel and DIN 1.2311 steel after pre-hardening?
As the representative steel grade of plastic mold steel, P20 and DIN 1.2311 are usually delivered in the pre-hardened condition, with a hardness of 280-340HB or 30-36HRC.The pre-hardened material has uniform hardness and can be directly used for mold-making processing.
What is the difference between P20 steel and P21 steel?
Although P20 and P21 steel belong to quenched and tempered plastic mold steel and have similar names, they are completely different.
First of all,P20 belongs to the chromium-molybdenum steel series, while P21 belongs to the precipitation hardening alloy steel of the Ni-Al-Cu series.The chemical composition they contain is also very different, as shown in the table below
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | V | Al |
| P20 | 0.28-0.4 | 0.2-0.8 | 0.6-1.0 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | 1.4-2.0 | 0.3-0.55 | - | - | - |
| P21 | 0.18-0.22 | 0.2-0.4 | 0.2-0.4 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | 0.2-0.3 | - | 3.9-4.25 | 0.15-0.25 | 1.05-1.25 |
In addition, P21 steel can be regarded as an improved version of P20 steel. Compared with it, P21 steel has better wear resistance, better polishing and more uniform hardness.
P20 Steel Pre hardened Treatment
The pre-hardening treatment we often say, here, for P20 steel, is quenching and tempering heat treatment.
First of all, quenching temperature is an important factor in P20 prehardening heat treatment.It will not only affect the grain size, but also further affect the final properties of the material, especially the toughness.For P20 steel for making large plastic molds, high toughness is required, and coarse grains are unfavorable.
| Quenching temperature,°C | 800 | 860 | 900 | 1000 | 1100 | 1200 |
| Grain Size | 8 | 7-8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 3-4 |
It can be seen from the above table that when the quenching temperature is 800-860°C, the grains are grade 7-8, which belongs to the fine grain structure, while when the quenching temperature is 1200°C, the grains are grade 3-4, and the coarse grains are severe.
Considering that the Ac3 of P20 is 815°C, the quenching temperature should be selected at about 860°C, so that not only higher hardness can be obtained, but also smaller grains can be guaranteed.
Quenching medium: For P20 steel, considering the good hardenability of the material, oil quenching can be used as the first choice.The maximum hardness after oil quenching is about 52HRC.
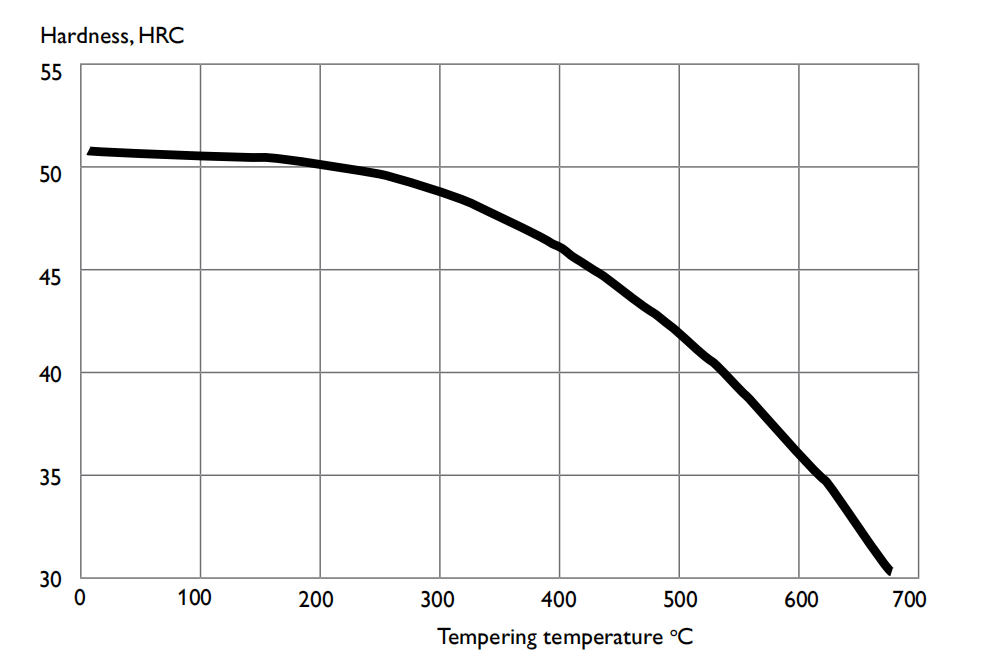
For the control of tempering temperature, the pre-hardening hardness of P20 is finally determined.The curve as below show the relationship between tempering temperature and hardness.
The hardness of P20 steel decreases with the increase of the tempering temperature, the carbide precipitation increases and gradually spheroidizes, aggregates and grows.The lath boundary gradually blurs, and some laths become wider after merging.This results in a decrease in hardness with increasing tempering temperature.
For P20, it is more appropriate to control the tempering temperature between 600-650°C,the tempering hardness is between 30-36HRC, which can meet the pre-hardening requirements.
P20 steel Mechanical properties at room temperature in Quenched & Tempered condition
| Tempering Temperature °C | Tensile Strength Mpa | Yield Strength Mpa | Elongation % | Reduction % | Impact Charpy J |
| 250 | 1850 | 1750 | 10.5 | 37.5 | 35 |
| 400 | 1680 | 1590 | 9 | 31 | 44 |
| 550 | 1360 | 1280 | 12 | 47.5 | 45 |
| 600 | 1185 | 1060 | 15 | 54.5 | 110 |
| 650 | 1080 | 950 | 17 | 60 | 120 |
| 675 | 1000 | 870 | 19.5 | 61.5 | 145 |
Introduction of Advanced Plastic Mould Steel: S136 and NAK80
What is S136 Steel?
S136 steel is the plastic mold steel grade of ASSAB company.As a high-grade stainless tool steel, it has a well-balanced combination of toughness, corrosion resistance and hardness.Its main features are as follows:
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Excellent polishability
- Excellent wear resistance
- Excellent hardenability
- Excellent toughness and ductility
Combining the advantages listed above, S136 steel grade has excellent production characteristics. Due to its excellent corrosion resistance, the benefits of using in plastic molds are outlined below:
- Lower maintenance cost
After the mold is used for a long time, the surface of the mold cavity still maintains the original smooth state. Molds do not require special protection when operated or stored in wet environments.
- Lower production cost
Since the mold cooling water channel is not affected by corrosion (unlike ordinary mold steel), the heat transfer characteristics and cooling efficiency remain stable during the life of the mold, ensuring a constant forming time of the mold.
The above benefits combined with the high wear resistance of the S136 provide low maintenance costs and long life molds for optimum economics.
S136 Steel Applications
S136 is recommended for all moulds, due to its special properties, it is more suitable for the needs of special environments.
- Corrosion and rust resistance: For the use of corrosive PVC, acetate and other injection molding materials or molds that must work and be stored in a humid environment.
- High smooth surface: production of optical products, such as cameras, sunglasses, chemical instruments and plastic products.
- Ductility and toughness: used for complex molds.
- Surface hardenability: high hardness requirements, important large molds
What is NAK80 Steel?
As a pre-hardened plastic mold steel, NAK80 is the patented steel of Japan Daido Steel Co., Ltd,and its pre-hardened hardness can reach 37-43HRC.As a popular steel, its characteristics are as follows:
- No need for heat treatment
- High purity of steel treated by vacuum degassing and refining
- Excellent wear resistance
- Good polishing performance
- Good machinability and etchability
- Excellent engraving and discharge performance
- Good weldability
NAK80 Steel Applications
NAK80 steel is generally used in mirror polishing molds, precision wrinkle processing molds, office automation equipment, auto parts EDM molds, and also used in transparent products or products that require a smooth finish, such as transparent product molds on automobiles, cameras, and computers.
- Efficient blanking dies, punching dies and imprinting dies
- All kinds of scissors, inlaid blades, woodworking blades
- Thread rolling die and wear-resistant sliding block
- Cold heading mold, thermosetting resin molding mold
- Deep drawing dies, cold extrusion dies
What is the difference between S136 and NAK80?
Before talking about the differences, let’s first talk about their similarities. These two are plastic mold steels with good polishing properties. They are generally used for high-precision plastic molds.
The main differences are as follows:
- Different hardness
NAK80 is a pre-hardened steel that has been pre-hardened to HRC38-42 and does not require heat treatment. The cutting performance of NAK80 will also be better, that is, good processing. S136 needs quenching and tempering and hardening treatment, and the hardness is above 48HRC.
- Difference in mirror polishing performance
NAK80 mirror polishing can reach 10000-12000 mesh, while S136 can reach 12000-18000 mesh after quenching and hardening.
- Difference in corrosion resistance
NAK80 is not anti-corrosion, and sometimes it will rust. If the plastic mold is used in a corrosive environment, it is not recommended to use NAK80, while S136 is corrosion-resistant,and it can be used for plastic molds in corrosive environments.
How to manufacture high quality P20/DIN 1.2311 steel?
In recent years, with the development of the plastics industry, plastic products tend to be larger and more complex, which puts forward higher requirements for the performance of plastic mold steel, especially P20/DIN 1.2311, which is the main grade of plastic mold steel.
What we need to face is how to manufacture high-quality P20/DIN 1.2311 steel, which is a very objective challenge.Here are a few key factors we can start with.
- Chemical Composition Control
In addition to certain strength and toughness, plastic mold steel also requires machinability, hardenability, wear resistance, corrosion resistance and mirror surface processing performance.
Considering the above situation, the chemical composition control of P20 steel must first meet the standard requirements, and then further balance and optimize the production cost economy and process performance of P20 steel.
- Metallurgical Quality Control
To manufacture high-quality P20 steel, the metallurgical quality of P20 steel must also meet the following requirements.
1. Macroscopic structure
| General Porosity(Grade) | Central Porosity(Grade) | Pattern Segregation(Grade) | General Spot Segregation(Grade) |
| ≤1.0 | ≤1.0 | ≤1.0 | not allowed |
2.Non-metallic Inclusions
| Non-metallic Inclusions | |||||||
| A | B | C | D | ||||
| Fine | Coarse | Fine | Coarse | Fine | Coarse | Fine | Coarse |
| Max 1.5 | Max 1.0 | Max 1.5 | Max 1.0 | Max 1.5 | Max 1.0 | Max 2.0 | Max 1.5 |
3.Gas content
| Oxygen,ppm | Hydrogen ,ppm | Nitrogen ,ppm |
| ≤20 | ≤2 | ≤50 |
- Heat Treatment Performance Control
The quenching and tempering heat treatment of P20 steel not only ensures the good mechanical properties of the material, but also obtains good hardness (HRC30-36), which provides a reliable guarantee for the cutting performance and mirror polishing performance of P20 steel.
The critical temperature of P20 steel is Ac1: 725°C, Ac3: 810°C, Ms: 280°C, the recommended quenching temperature of P20 steel is 860-880°C, oil cooling, tempering temperature 600-650°C.
WHERE CAN YOU BUY HIGH QUALITY P20/DIN1.2311 STEEL?
We often hear complaints from customers that the purchased P20 steel does not match the composition and hardness.What is even more annoying is that after the material is finally made into a finished mold, the use effect is not ideal, resulting in a waste of a lot of manpower, material resources and time costs.
We empathize with customers’ feedback, here we guarantee that the P20 steel we produce can fully meet customer needs,because we have rich manufacturing experience,and a complete set of quality reports and after-sales support services.We believe that our profession can completely solve problems for customers.
What We Supply For P20/DIN 1.2311 Steel
- Hot Rolled Round Bar:Φ16-Φ130mm
- Hot Forged Round Bar:Φ80-Φ1000mm
- Customized service:Special Size & Length
- Delivery Condition: Quenched & Tempered
- Free Sample of P20/DIN 1.2311 Steel