S355J2G3 steel is a carbon manganese ,high yield non alloy steel. It is called S355 because of the average minimum yield for this material is 355 Mpa.As a structural steel,it has excellent strength and weldability.It can be readily welded to other weldable steel. For its low carbon equivalent, it possesses good cold-forming properties. S355J2G3 is generally supplied in a normalized condition.
1.S355J2G3 steel Supply Form & Size &Tolerance
| Form of Supply | Size(mm) | Length(mm) |
| Round bar | Φ140-Φ1000 | 3000-10000 |
| Square bar | 100 x 100-600x600 | 3000-6000 |
Flat bar/Blcoks | Thickness :120-800 | 2000-6000 |
| Width:120-1500 |
| Surface Finish | Black for Forged condition | Rough Turned |
| Tolerance | (0,+5mm) | (0,+3mm) |
Remark:All the size supplied in Forged condition
2.Chemical Composition & Related Specifications
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S |
| S355J2G3 | ≤ 0.22 | ≤0.55 | ≤1.6 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 |
| Germany | UK | China | Japan |
| ST52-3/1.0570 | En14A/150M19 | 16Mn | SM 490 |
3.Popular S355 specifications
| Grade | symbol | |
S355 | JR | Charpy impact tests at room temperature 20°C |
| J0 | Charpy impact tests at 0°C | |
| J2 | Charpy impact tests at -20°C | |
S355J2 | N | Supply condition normalised |
| G3 | Supply condition normalised | |
4. Mechanical Property
| Thickness ,mm | 5-100 | 100-150 | |||||||
| Tensile strength,Mpa | 470-630 | 450-650 | |||||||
| Thickness ,mm | ≤ 16 | 16-40 | 40-63 | 63-80 | 80-100 | 100-150 | 150-200 | 200-350 | > 250 |
| Yield strength,Mpa | ≥ 355 | ≥ 345 | ≥ 335 | ≥ 325 | ≥ 315 | ≥ 295 | ≥ 285 | ≥ 275 | ≥ 265 |
| Thickness ,mm | 5-40 | 40-63 | 63-100 | 100-150 | |||||
| Elongation,% | ≥20 | ≥19 | ≥18 | ≥18 | |||||
| Impact,J | J2: 27J at - 20°C | ||||||||
5.Normalizing
Normalizing is used to refine the structure of forgings that might have cooled non-uniformly after forged,and considered as a conditioning treatment before final heat treatment.Normalizing temperature for S355J2G3 steel should be carried out between 890℃-950℃. hold suitable time for the steel to be thoroughly heated to complete the ferrite to austenite transformation.Cool in still air.
6.Application
S355J2G3 is a low carbon structural steel grade often used for application which require better mechanical properties than that of S275 and S235 grade.It is widely used in engineering and construction industries.
Applications include axles, bolts and connecting rods, motor, hydraulic and pump shafts, machinery parts,transmission towers, dump trucks, cranes, trailers, bull dozers, excavators, forestry machines, railway wagons, dolphins, penstocks, pipes, highway bridges, building structures, oil and gas platforms, offshore structures, shipbuilding, power plant, palm oil equipments and machineries, fans, pumps, lifting equipments and port equipments etc.
S355J2G3 STEEL BUYING GUIDE
When we need to find information about S355J2G3 Steel on the Internet, we will definitely see a lot of related information about it, such as S355JR, S355J0, S355J2, S355J2+N, etc. Do you feel confused, what does it mean?
Don’t worry, through our guide, we will help you sort out the relevant knowledge about S355J2G3 steel.By learning, you can definitely master everything about it, so as to help you buy high-quality S355J2G3 materials.
Well, a journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step, let’s get started.

WHAT IS S355J2G3 STEEL?
The steel numbers of the DIN17006 system are divided into two types: according to the material strength and according to the chemical composition. The expression method according to the chemical composition is applicable to non-alloy steel, alloy steel and high-alloy steel,
While the representation method by material strength is only applicable to non-alloy steel, and its representation method is listed in Table 1 below.
| Standard | Representation | Code and Number Description |
DIN old standard | StXX UStXX RStXX QStXX | St:Steel XX:Indicates the lower limit of tensile strength(Kgf/mm2) Ust: Rimmed steel RSt:Killed Steel QSt:Cold heading steel |
EN10025 | SXXX | S:Structural steel XXX:The three digits represent the lower limit of yield strength(Mpa) |
The meaning of special symbols in S355 steel
| Symbol | Meaning |
| J0 | Longitudinal Charpy V-notch impacts 27J at 0°C |
| J2 | Longitudinal Charpy V-notch impacts 27J at -20°C |
| K2 | Longitudinal Charpy V-notch impacts 40J at -20°C |
| AR | Supply condition as Rolled |
| N | Supply condition as Normalized or Normalized Rolled |
| G3/G4 | Deoxidation measure |
From the above information, S355J2G3 steel can be described as a non-alloy structural steel with a yield strength of not less than 355MPa, the delivery state is fully killed and normalized, and the -20°C longitudinal impact energy is not less than 27J.
IS S355J2G3 STEEL SAME AS Q355D STEEL?
First of all, S355J2G3 and Q355D are both structural steels.As an international equivalent steel grade, S355J2G3 belongs to the European standard EN10025, while Q355D comes from China’s GB/T 1591 standard.Although they belong to different standards, there must be similarities and differences between them. Next, let’s compare them in detail.
- Chemical composition
| Standard | Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu |
| EN10025 | S355J2G3 | ≤0.22 | ≤0.55 | ≤1.6 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | - | - | - |
| GB/T 1591 | Q355D | ≤0.22 | ≤0.55 | ≤1.6 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.4 |
It can be clearly seen from the above table that S355J2G3 and Q355D are consistent in C, Si, Mn elements. In the control of P, S harmful elements, Q355D is better than S355J2G3.For residual elements, such as Cr, Ni, Cu, etc., Q355D has stricter control requirements than S355J2G3.
Therefore, in terms of chemical composition, Q355D can completely replace S355J2G3.
- Mechanical Property
Tensile Strength Comparison
| S355J2G3 | Q355D | ||
| Thickness ,mm | Tensile Strength,Mpa | Thickness ,mm | Tensile Strength,Mpa |
| <3 | 510-680 | - | - |
| 3-100 | 490-630 | <100 | 470-630 |
| 100-150 | 470-630 | 100-150 | 450-600 |
| 150-250 | 450-630 | 150-250 | 450-600 |
| - | - | 250-400 | 450-600 |
Yield Strength Comparison
| S355J2G3 | Q355D | ||
| Thickness ,mm | Yield Strength,Mpa | Thickness ,mm | Yield Strength,Mpa |
| <16 | ≥355 | <16 | ≥355 |
| 16-40 | ≥345 | 16-40 | ≥345 |
| 40-63 | ≥335 | 40-63 | ≥335 |
| 63-80 | ≥325 | 63-80 | ≥325 |
| 80-100 | ≥315 | 80-100 | ≥315 |
| 100-150 | ≥295 | 100-150 | ≥295 |
| 150-200 | ≥285 | 150-200 | ≥285 |
| 200-250 | ≥275 | 200-250 | ≥275 |
| - | - | 250-400 | ≥265 |
Elongation Comparison
| S355J2G3 | Q355D | ||
| Thickness ,mm | Elongation,% | Thickness ,mm | Elongation,% |
| 3-40 | L:≥22 T:≥20 | <40 | L:≥22 T:≥20 |
| 40-63 | L:≥21 T:≥19 | 40-63 | L:≥21 T:≥19 |
| 63-100 | L:≥20 T:≥18 | 63-100 | L:≥20 T:≥18 |
| 100-150 | L:≥18 T:≥18 | 100-150 | L:≥18 T:≥18 |
| 150-250 | L:≥17 T:≥17 | 150-250 | L:≥17 T:≥17 |
| - | - | 250-400 | L:≥17 T:≥17 |
Impact Energy Comparison
| S355J2G3 | Q355D | ||||
Temperature,°C | Impact,J | Temperature,°C | Impact,J | ||
| Longitudinal | Transverse | Longitudinal | Transverse | ||
| -20°C | ≥27 | - | -20°C | ≥34 | ≥27 |
From the above performance comparison table, it can be seen that the difference between S355J2G3 and Q335D in tensile, yield, and elongation is very small, which can be basically regarded as the same.
In terms of impact performance requirements, Q355D not only requires higher longitudinal impact value than S355J2G3, but also additionally adds lateral impact requirements, which are significantly higher than S355J2G3.
- Welding performance
As structural steel, S355J2G3 and Q355D steel will inevitably involve welding in the application process.The welding performance of S355J2G3 and Q355D can be evaluated by calculating their carbon equivalent value (CEV).
CEV=C+Mn/6+(Cr+Mo+V)/5+(Ni+Cu)/15.
| S355J2G3 | Q355D | ||
| Thickness ,mm | CEV | Thickness ,mm | CEV |
| <40 | 0.45 | <30 | 0.45 |
| 40-150 | 0.47 | 30-150 | 0.47 |
| 150-250 | 0.49 | 150-250 | 0.49 |
| - | - | 250-400 | 0.49 |
| Carbon equivalent (CE) | Weldability |
| ≤0.35 | Excellent |
| 0.36–0.40 | Very good |
| 0.41–0.45 | Good |
| 0.46–0.50 | Fair |
| ≥0.5 | Poor |
It can be seen from the above table that the welding performance of S355J2G3 and Q355D steel is good. As long as a reasonable welding process is used, a welding product with reliable quality can be obtained.
QUICK FAQS FOR S355J2G3 STEEL
Is S355J2G3 steel alloy steel?
In fact, according to the chemical composition of S355J2G3, it is difficult to classify it as alloy steel. According to the division of European standards EN10025 and EN10250, S355J2G3 is defined as unalloyed structural steel.
Is S355J2G3 steel easy to weld?
The alloy content of S355J2G3 steel is very small, its carbon equivalent is 0.345~0.491, and the weldability is good, and preheating is generally not necessary before welding.
However, since the hardening tendency of S355J2G3 steel is slightly larger than that of low carbon steel, preheating measures should be taken to prevent cold cracks when welding at low temperature (such as open-air operation in winter) or when welding on large rigid and thick structures.
The preheating temperature of S355J2G3 steel under different plate thicknesses and different ambient temperatures is shown in the table below.
| Thickness,mm | Preheating temperature at different temperatures |
| <16 | No preheating above -10℃, preheating 100~150℃ below -10℃ |
| 16-24 | No preheating above -5℃, preheating 100~150℃ below -5℃ |
| 25-40 | No preheating above 0℃, preheating 100~150℃ below 0℃ |
| >40 | Preheating 100~150℃ |
Can S355J2G3 Steel be Case Hardened?
Due to the low carbon content of S355J2G3, it is difficult to obtain good hardness by direct quenching.However, good hardness can be obtained by case hardening methods such as carburizing and nitriding.
After carburizing and quenching, the hardness of S355J2G3 steel can usually reach above 40HRC.By nitriding, the surface hardness of S355J2G3 can reach 530-700HV3, Nitration hardness depth 0.2-0.8mm.
What is S355J2G3 steel used for?
S355J2G3 steel has good comprehensive mechanical properties, low temperature impact toughness, cold stamping properties and machinability.
S355J2G3 steel is widely used in welded structures subjected to dynamic loads, such as bridges, vehicles, ships, pipelines, boilers, large vessels, oil tanks, heavy machinery, mining machinery and cryogenic pressure vessels.
S355J2G3 Steel VS A572Gr50 Steel
A572GR50 steel is defined as high-strength low-alloy Columbium-Vanadium structural steel which belongs to ASTM A572 standard.According to the standard, structural steel is divided into five grades, namely Grade42, Grade50, Grade55, Grade60 and Grade65.Among them, Grade50 corresponds to S355J2G3, as the international equivalent steel grade.
| Standard | Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Nb | V |
| EN10025 | S355J2G3 | ≤0.22 | ≤0.55 | ≤1.6 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | - | - |
| ASTM A572 | Grade50 | ≤0.23 | ≤0.4 | ≤1.35 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | 0.005-0.05 | 0.01-0.15 |
From the above chemical composition comparison,We know that S355J2G3 and A572Gr50 steel have certain differences in Mn, Nb, and V elements.Due to the difference in chemical elements, S355J2G3 is defined as a non-alloyed structural steel, while A572GR50 is defined as a low-alloyed structural steel due to the presence of Nb, V.
In terms of mechanical properties, as equivalent steel grades, their requirements on yield strength are basically the same.For low temperature impact requirements, S355J2G3 is mandatory, while A572GR50 needs to be negotiated with customers.
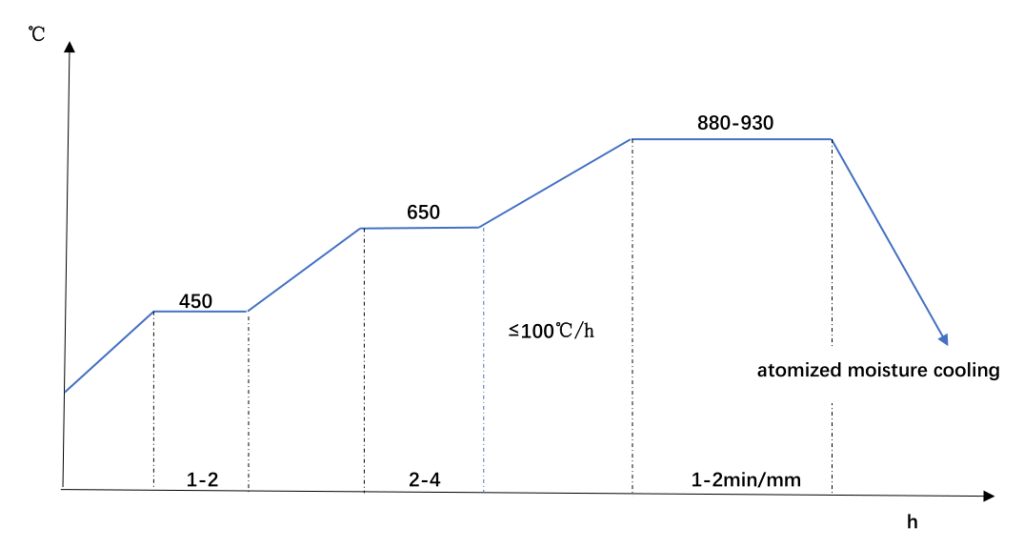
HOW TO NORMALIZING S355J2G3 STEEL?
As a low carbon structural steel, S355J2G3 steel is usually normalized as the final heat treatment in most applications.How to complete the normalizing of S355J2G3 steel efficiently and with high quality, the following factors must be considered.
S355J2G3 Forged round steel Normalizing
- Heating Rate
In the normalizing heat treatment process, is it necessary to control the heating rate?Our answer is yes!
The heating rate has a great relationship with the structure of S355J2G3 steel. When heating, the possibility of deformation and cracking caused by the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the workpiece should be considered.
For S355J2G3 workpieces with large wall thickness or complex shapes, it is especially necessary to control the heating rate. If it is too fast, it will cause cracking and scrap under the action of thermal stress. Of course, it can’t be too slow, which will cause excessive heating loss and serious oxidation or decarburization on the surface of the workpiece.
In the early stage when the temperature is low, the temperature rise can be faster. After the temperature rises to a certain extent, the temperature rise speed must be controlled. The temperature rise speed is controlled at 50-100°C/h.
- Heating Temperature
The heating temperature, that is, the normalizing temperature, is to heat the workpiece to 30~50°C above Ac3, the purpose is to convert all the ferrite structure in the steel into austenite and make it completely austenitized.
If the temperature is too low, the steel cannot be completely austenitized, resulting in an uneven structure, which in turn affects the material properties.If the temperature is too high, the austenite grains in the steel will grow excessively, and it is easy to produce a coarse Widmandarin structure, which will lead to a decrease in the plasticity and toughness of the material.
- Holding Time
The holding time has a great relationship with the effective section thickness of the material, the heating method, the amount of furnace loading and the furnace loading method.
In short, a reasonable holding time should ensure that the material is fully heated and evenly heated.Too long or too short holding time will directly affect the further use of the material.Therefore, it should be flexibly applied in actual production to achieve rational and efficient maximum utilization of resources.
- Cooling Rate
The cooling rate is an important indicator of the normalizing process.In normalizing, not only control the heating rate, but also strictly control the cooling rate after heat preservation.
The cooling rate of normalizing is much faster than that of annealing, so the obtained structure is also finer, and the mechanical properties are also improved.
The normal cooling method of normalizing is air cooling. When a faster cooling speed is required, air cooling, fog cooling, water cooling and other methods can also be used to speed up the cooling.
S355J2G3 Steel Normalizing Diagram
S355J2G3 Steel Mechanical Property in Normalized conditon
| Size, mm | Tensile, Mpa | Yield, Mpa | Elongation, % | Reduction, % | Charpy Impact, J | Hardness, HB | Sample location |
| Φ330 | 532 | 330 | 23 | 56 | -20℃,27/30/30 | 151/148/159 | 80mm,Transverse |
| Φ350 | 545 | 318 | 26 | 54 | -20℃,33/30/27 | 183/152/188 | 80mm,Transverse |
| Φ370 | 501 | 318 | 26 | 54 | -20℃,33/27/37 | 151/150/179 | 80mm,Transverse |
| Φ410 | 510 | 309 | 34 | 58 | -20℃,52/60; -40℃,49 | 133/143/136 | 1/3 Radius |
Remark:The above data is the actual test value, for reference only
WHERE CAN YOU BUY HIGH QUALITY S355J2G3 STEEL?
As the most common structural steel, there is no doubt that we believe that customers can easily find S355J2G3 steel, because it can be seen everywhere in the market.But then customers may be worried, how to choose?
Here, customers can choose the size you want with confidence, because we will provide a complete set of quality reports and follow-up supporting services.We believe that the customer’s experience of selecting materials is the same as supermarket shopping, which can be seen and touched.
What We Supply For S355J2G3 Steel
- Hot Rolled Round Bar:Φ20-Φ350mm
- Hot Forged Round Bar:Φ80-Φ1000mm
- Customized service:Special Size & Length
- Free Sample of S355J2G3 Steel
Heat Treatment
- Normalized(+N)
Machining
Turning/Milling/Drilling/Peeling/Polishing