When “Iron Man” Wears 4140 Armor,The “All-round Warrior” in the industrial field
Imagine the following scenes:
- A 50-ton mining truck is driving in a bumpy mine pit, and the drive shaft is subjected to 3,000 torque shocks per minute;
- A civil airliner lands at a speed of 300 kilometers per hour, and the landing gear instantly absorbs hundreds of tons of impact force;
- A set of injection molds continuously presses plastic parts 100,000 times at a high temperature of 200℃, and the surface of the mold core is still as smooth as new.
Behind these scenes, there is a common “invisible guardian” – 4140 steel.
Data speaks:
- The world consumes more than 2 million tons of 4140 steel each year, and 60% of the key components of heavy machinery rely on it;
- In the selection of “Material Today”, it ranks third in the “Top Ten Industrial Materials of the 21st Century”.
Why can it conquer extreme working conditions from automobiles to aerospace? Today, we dissect its “all-round gene”.
1. Where does the “Superpower” of 4140 Steel Come From?
1.1 Chemical composition: the “golden formula” of the steel industry
Basic elements:
- Carbon (0.38-0.43%): strengthens hardness, but excessive amounts will reduce toughness;
- Chromium (0.8-1.1%): improves hardenability and corrosion resistance;
- Molybdenum (0.15-0.25%): refines grains and increases high-temperature strength.
Trace additions:
- Manganese (0.75-1.0%): deoxidizer, reduces hot brittleness;
- Silicon (0.15-0.35%): increases elastic limit.
Key conclusion: The combination of chromium and molybdenum makes the hardening depth of 4140 3 times higher than that of ordinary carbon steel, and a cross-section of 100mm can still be hardened evenly!
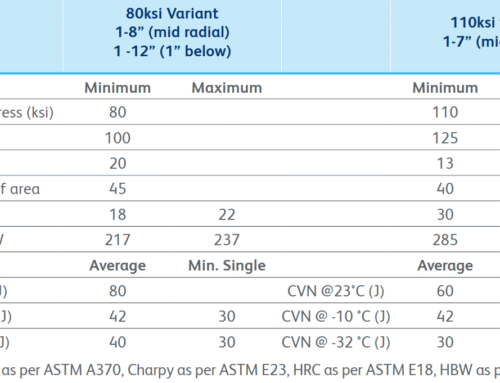
1.2 Performance parameters: Tough guys also have tenderness
| Performance | Typical value | Compared with ordinary 1045 steel |
| Tensile strength | ≥950 MPa | ↑40% |
| Yield strength | ≥650 MPa | ↑50% |
| Impact energy (normal temperature) | ≥40J | ↑200% |
| Hardness (quenched and tempered) | HRC 28-32 | ↑30% |
Engineer’s comments:
“4140 has a nearly perfect balance of strength and toughness – it will not break like high carbon steel, nor will it be soft like low carbon steel, making it an ideal choice for load-bearing parts.” ——Head of the material laboratory of a heavy industry group
2. The “Ultimate Form” of 4140 Steel is Determined By Heat Treatment
2.1. Standard process chain: from “blank” to “God of War”
- Normalizing (850-900℃): eliminate forging stress and make the structure uniform;
- Quenching (830-860℃ oil cooling): obtain high-hardness martensite;
- Tempering (adjusted according to demand):
– Low-temperature tempering (200-300℃): hardness HRC 50-55, suitable for wear-resistant parts;
– High-temperature tempering (500-600℃): hardness HRC 28-32, with the best comprehensive performance.
⚠️Fatal misunderstanding: Blind pursuit of high hardness (such as no tempering after quenching) will lead to brittle fracture of parts!
2.2 Industry Customized Solutions
- Oil Drill Pipe: Adopting “Secondary Tempering” (550℃×2h), the ability to resist hydrogen sulfide stress corrosion is increased by 60%;
- Gear Surface Strengthening: First tempering to HRC 30, then ion nitriding, the surface hardness can reach HV 1100!
3. The Battlefields Where 4140 Steel Conquers The World,Why is it Everywhere?
Battlefield 1: Automobile transmission system
- Case: The transmission shaft of a German heavy truck brand uses 4140 steel. By optimizing the heat treatment process, the fatigue life is increased from 500,000 times to 800,000 times;
- Secret: Use “sub-temperature quenching” (780℃ oil cooling + 600℃ tempering) to reduce deformation while ensuring strength.
Battlefield 2: Aviation landing gear
- Challenge: When the aircraft lands, the landing gear needs to withstand an impact of up to 5 times its own weight;
- Solution: 4140 forgings are vacuum quenched + cryogenically treated, and the impact toughness is increased by 25%.
Battlefield 3: Hydraulic valve block
- Pain point: Traditional cast iron valve body is prone to bursting;
- Innovation: 4140 steel valve body with surface chrome plating, the pressure resistance exceeds 70MPa.
4. The “Nemesis” & Substitutes of 4140 Steel
4.1 When should 4140 not be used?
- Low temperature environment (<-40℃): Toughness decreases, and nickel-containing 4340 steel needs to be used instead.
- Strong acid environment: Insufficient corrosion resistance, it is recommended to upgrade to duplex stainless steel 2205.
4.2 Cost-effectiveness: 4140 vs 5140
| Index | 4140 | 5140 |
| Tensile strength | 950MPa | 800MPa |
| Relative price | x1.0 | x0.67 |
| Applicable scenarios | Heavy-duty parts | Ordinary shafts |
The purchasing director suggested: “If the budget allows, the life cycle cost of 4140 is lower – its replacement frequency is 50% lower than that of 5140.”
5. Controversy & The Future: Will 4140 Steel be Replaced?
- Opponents: “Carbon fiber and ceramic-based composite materials will replace traditional steel!”
- Supporters: “4140’s process maturity, repairability and cost advantages are irreplaceable within 20 years!”
Our objective view: Before the new material is fully popularized, 4140 will still be the “price-performance king” of medium and high load components.4140 steel has engraved the trajectory of industrial development with strength and integrated into every corner with its omnipotence. I believe that in the future when science and technology continue to advance, it will unlock more applications and continue to write a glorious chapter.
Interactive topic: What problems have you encountered when using 4140 steel? Please contact us and discuss together!