1.2329 steel (corresponding to DIN standard, similar to H11 steel in the United States) is a hot working die steel. It is widely used in many industrial fields for its excellent high temperature strength, wear resistance, toughness and thermal fatigue resistance. The following are its specific applications and cases:
Versatile Applications in Modern Industry
1. Die-casting molds
- Application scenarios: Die-casting molds for manufacturing non-ferrous metals such as aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, and zinc alloys.
- Industry cases:
– Automotive industry: die-casting of engine blocks, gearbox housings, wheels, and other parts.
– Electronics industry: production of precision parts such as radiators and connectors. - Advantages: Under the repeated impact of high-temperature molten metal, it can still maintain stable size and resistance to thermal cracking.
2. Hot extrusion molds
- Application scenarios: hot extrusion molding of materials such as copper alloys and aluminum alloys.
- Industry cases:
– Construction industry: production of aluminum profiles (door and window frames, curtain wall structures).
– Industrial parts: processing of complex cross-section profiles such as heat sinks and pipes. - Advantages: high temperature softening resistance, long mold life, suitable for continuous high-pressure operation.
3. Plastic injection molds
- Application scenarios: injection molding of high-temperature engineering plastics (such as PEEK and nylon).
- Industry cases:
– Automobile: high temperature resistant lampshades, intake manifolds.
– Consumer electronics: mobile phone casings, laptop computer structural parts. - Advantages: high surface hardness, ensuring mold finish, reducing plastic parts demolding defects.
4. Hot forging molds
- Application scenarios: hot forging of steel or alloys (such as hammer forging, press forging).
- Industry cases:
– Mechanical manufacturing: key forgings such as gears, crankshafts, connecting rods, etc.
– Aerospace: high-temperature forging of turbine discs and landing gear components. - Advantages: high toughness to resist impact loads, heat fatigue resistance to reduce mold cracking.
5. Stamping and shearing molds
- Application scenarios: stamping or shearing of high-temperature plates.
- Industry cases:
– Stainless steel kitchenware: hot stamping of pots and knives.
– Energy industry: precision shearing of high-temperature alloy plates. - Advantages: maintaining hardness at high temperatures, reducing edge wear, and extending maintenance cycles.
6. Wear-resistant parts and machine tools
- Application scenarios: tools and parts in high-temperature and high-wear environments.
- Industry cases:
– Glass manufacturing: glass molds and conveyor rollers.
– Metallurgical industry: rolling rollers, guide devices. - Advantages: Through heat treatment (such as quenching + tempering), the surface hardness is increased to 50-54 HRC, and the wear resistance is significant.
7. Special structural parts
- Application scenarios: Mechanical parts that need to have both high temperature strength and toughness.
- Industry cases:
– Chemical equipment: high temperature valves, fasteners.
– Energy field: gas turbine blade base. - Advantages: Maintain high strength at 500-600℃ to avoid creep deformation.
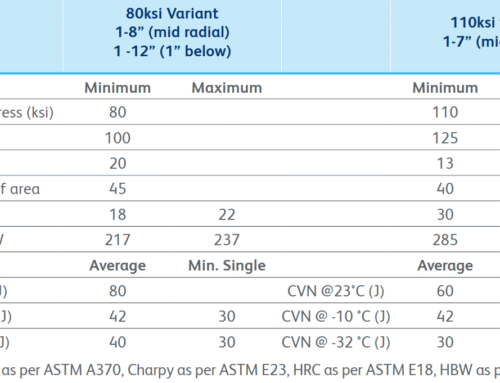
1.2329 Steel Material Properties Support Applications
- Thermal fatigue resistance: resists crack propagation under frequent alternation of hot and cold, suitable for die casting and hot forging.
- High toughness: adds chromium, molybdenum and vanadium elements to improve impact resistance.
- Processing performance: easy to cut in the annealed state, reducing mold manufacturing costs.
1.2329 Steel Comparison With Other Materials
- Comparison with H13 (1.2344): 1.2329 has a lower carbon content and better toughness, but slightly lower high temperature hardness, and is suitable for higher impact load scenarios.
- Comparison with ordinary tool steel: High temperature resistance is significantly improved, and the mold life is extended by 3-5 times.
Summary
Due to its comprehensive performance, 1.2329 steel has become an ideal choice for high temperature and high stress environments, especially in automotive die casting, aluminum extrusion and precision plastic molds. Correct application can greatly improve production efficiency and reduce the frequency of mold replacement.