1.2343 steel is a classic, reliable, and exceptionally well-balanced hot work die steel, belonging to the German standard (DIN) designation. Internationally, its most widely known equivalent designation is H11 (American standard AISI/SAE).
With its outstanding toughness as its core competitive advantage, 1.2343 steel combines excellent resistance to thermal fatigue, heat treatment stability, and machinability, making it one of the preferred materials for die casting, hot forging, hot extrusion, and high-end plastic molds. When selecting materials for mold design, 1.2343 steel is always a strong candidate when “toughness” and “resistance to thermal fatigue” are listed as the most critical indicators.

1.2343 STEEL CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | V | Mo |
| 1.2343 | 0.36-0.42 | 0.9-1.2 | 0.3-0.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 4.8-5.5 | 0.25-0.5 | 1.1-1.4 |
| H11 | 0.33-0.43 | 0.8-1.25 | 0.2-0.6 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 4.75-5.5 | 0.3-0.6 | 1.1-1.6 |
1.2343 STEEL EQUIVALENT GRADE
- China: 4Cr5MoSiV
- USA: H11
- Japan: SKD6
- British : BH11
- Europe: X37CrMoV5-1
1.2343 STEEL PHYSICAL PROPERTY
- Density: 7.80 g/cm³
- Thermal conductivity: 25-28.5 W/m・K (20℃)
- Coefficient of thermal expansion: 12.5×10⁻⁶/K (20-300℃)
- Elastic modulus: 210 kN/mm²
1.2343 STEEL FORGING
- Preheating temperature: 700-750℃, hold for 1-2 hours, heating rate ≤100℃/h
- Initial forging temperature: 1050-1100℃ (optimal 1065-1080℃, not exceeding 1120℃ to prevent overheating)
- Final forging temperature: ≥850℃ (never lower than 800℃ to prevent work hardening and cracking)
- Forging Ratio:above 4:1
- Cooling method: Furnace cooling (air cooling is strictly prohibited) to ensure slow and uniform cooling.
- Post-Forging Treatment:After forging, 1.2343 steel requires annealing heat treatment at 820-840℃ (holding for 2-4 hours), followed by furnace cooling to ≤500℃ (≤30℃/h), and then air cooling.
QUICK FAQS FOR 1.2343 STEEL
How is the high-temperature resistance of 1.2343 steel?
1.2343 steel has excellent high-temperature stability, with a working temperature of up to 600-650℃ and a high-temperature hardness of HRC 45-50, making it less prone to softening and failure.
What is the toughness of 1.2343 steel?
1.2343 steel exhibits excellent overall toughness with balanced toughness in all directions, reducing the risk of stress concentration. Compared to similar hot-work steels such as 1.2344/H13, its toughness is more prominent, making it less prone to fracture under impact loads and extending the service life of molds.
How is the thermal fatigue resistance of 1.2343 steel?
1.2343 steel exhibits excellent resistance to thermal fatigue. Due to its low sensitivity to rapid temperature changes, 1.2343 steel is less prone to hot cracking during repeated thermal cycling.
What is the machinability property of 1.2343 steel?
1.2343 steel possesses excellent machinability, allowing for easy forming processes in its soft-annealed condition, making it suitable for complex mold manufacturing.
Is 1.2343 steel easy to polish?
1.2343 steel exhibits excellent polishing performance, enabling high-gloss surface treatments, making it suitable for molds with stringent surface finish requirements.
Can 1.2343 steel be nitrided?
1.2343 steel can have its surface wear resistance further improved through nitriding treatment, meeting the requirements of precision components.
1.2343 STEEL HEAT TREATMENT
1.2343 Steel Annealing
| Process | Softening Annealing | Spheroidizing Annealing | Stress-relief Annealing |
| Temperature | 820-840℃ | 860-890℃×3h→ 730-750℃×4h Isothermal | 600-650℃ |
| Cooling Method | Furnace cooling | Furnace cooling | Furnace cooling |
| Result | Target Hardness: ≤229HB (Improves machinability) | Hardness after annealing: ≤205HB, uniform spherical pearlite structure, further improving machinability | Eliminates residual stress from machining, preventing deformation and cracking |
1.2343 Steel Quenching
- Preheating:Stage 1: 400-450℃ (hold for 1-2 hours);Stage 2: 850-880℃ (hold for 1-2 hours)
- Austenitizing Temperature: 1000-1030℃ (Optimal 1020℃)
- Holding Time: Calculated per section (30 minutes per 25mm section, minimum ≥30 minutes)
- Cooling Method: Oil cooling or air cooling (for sections ≤150mm, air cooling to full hardness is possible)
- Quenching Hardness: Approximately 58-62 HRC
1.2343 Steel Tempering
- Temperature range: 530-680℃ (select according to performance requirements)
- Tempering cycles: at least twice (three times for important molds), with an interval of ≥24 hours between each cycle
- Holding time: ≥2 hours + an additional 1 hour for every 25mm thickness
- Heating/Cooling: slow heating (≤100℃/h), air cooling after removal from the furnace
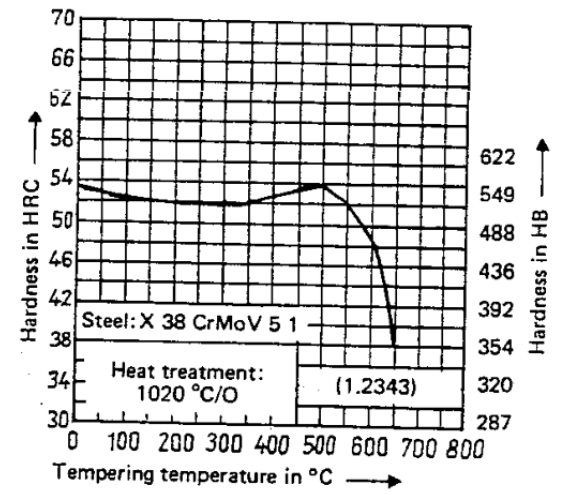
DIN 1.2343 Steel Tempering vs Hardness Diagram
1.2343 Steel Tempering Temperature and Property & Application Relationship
| Tempering Temperature | Hardness | Applicable Scenarios |
| 160-180°C | 58-62HRC | Cold stamping dies, tools requiring high hardness |
| 300-350°C | 52-54HRC | Dies requiring medium hardness and toughness |
| 530-560°C | 50-53HRC | General-purpose hot work dies (die casting, extrusion) |
| 580-620°C | 48-50HRC | Dies for high-temperature conditions (heat fatigue resistance) |
| 650-680°C | 40-45HRC | Heavy-duty dies requiring extremely high toughness |
1.2343 Steel vs. Similar Materials
- vs. 1.2344 (H13): 1.2344 (containing approximately 5% chromium and 1.0% vanadium) has slightly better wear resistance and high-temperature strength than 1.2343, but slightly lower toughness. 1.2343 is preferred for applications subjected to severe impacts or highly sensitive to cracking due to its higher toughness.
- vs. 1.2714 : The latter is a traditional tungsten-based hot-work die steel with higher hot strength but lower toughness and resistance to thermal fatigue than 1.2343, and is more expensive. 1.2343 has replaced it in many applications.
- vs. 1.2367 (H10): Its composition and properties are very close to 1.2343, and they are sometimes used interchangeably.
DIN 1.2343 STEEL SUPPLY FORM & SIZE & TOLERANC
Round bar:Φ12-Φ1000mm
Flat bar:Thickness :8-600mm ,Width:200-1100mm
| Surface Finish | Black-Forged | Black-Rolled | Rough Turned | Cold Drawn | Peeled | Polished | Grinded |
| Tolerance | 0/+5mm | 0/+1mm | 0/+3mm | Best H11 | Best H9 | Best H9 | Best h8 |