1.2714 tool steel,also refers to 56NiCrMoV7 as per German standard DIN 17350.It is improved on the basis of 1.2344 steel, which not only retains the advantages of 1.2344 high plasticity, high toughness and wear resistance, but also has better heat crack resistance.
1.2714 steel not only has good toughness, ductility and crack resistance, but also has high hardenability. The martensite structure can be obtained by air cooling during quenching.After quenching and tempering, 1.2714 steel has small deformation and excellent comprehensive performance.It is suitable for large-scale, complex, precise and long-life die-casting molds, high-performance die-casting molds, extrusion molds, etc.

CHEMICAL COMPOSITION AS PER DIN 17350
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | V |
| 1.2714/56NiCrMoV7 | 0.50-0.60 | 0.1-0.4 | 0.65-0.95 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | 1.0-1.2 | 1.50-1.8 | 0.45-0.55 | 0.07-0.12 |
1.2714/56NiCrMoV7 EQUIVALENT NATIONAL GRADE
As a member of hot work die steel, 1.2714 steel is highly affirmed by technical engineers all over the world for its excellent hot workability, and has developed similar grades that meet the needs of their respective countries.
| Standard | Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | V |
| ASTM A681 | AISI L6 | 0.65-0.75 | 0.1-0.5 | 0.25-0.80 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | 0.6-1.2 | 1.25-2.0 | ≤0.50 | — |
| EN ISO 4957 | 55NiCrMoV7 | 0.50-0.60 | 0.1-0.4 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.02 | 0.8-1.2 | 1.50-1.8 | 0.35-0.55 | 0.05-0.15 |
| JIS G4404 | SKT4 | 0.50-0.60 | 0.1-0.4 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.02 | 0.8-1.2 | 1.50-1.8 | 0.35-0.55 | 0.05-0.15 |
1.2714/56NiCrMoV7 FORGING PROCESS
Ingot Quality Control
When we forge 1.2714 steel, the first consideration is the quality of the forged steel ingot, which requires us to choose a suitable steelmaking process to control the quality of the billet.
The ingot process for 1.2714/56NiCrMoV7 as below:
Electric Arc Furnace(EAF)→Secondary Refining(LF)→ Vacuum Decarburization(VD)→Ingot Casting
Forging Temperature Control
- Initial Forging Temperature:1100-1150oC
- Heating temperature control:Heating up and holding temperature in stages to ensure that 1.2714 steel is heated evenly.
- Final Forging Temperature:≥850oC
Forging Deformation
When we consider the amount of forging deformation, the first thing that comes to mind is the forging ratio.Through the forging process, an appropriate forging ratio can promote the bubbles, porosity, and micro-cracks in the steel ingot to be welded under the action of compressive stress, and the material density is improved.
For 1.2714 steel,we usually control the forging ratio with Upsetting and Drawing Process,and guarantee it above 4:1
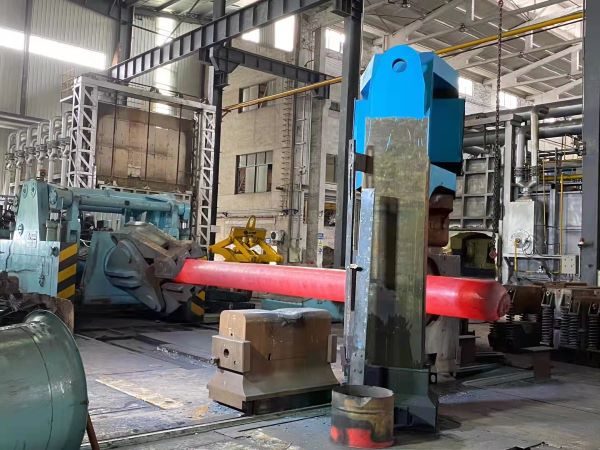

DIN1.2714 Steel Hot Foring with 1600T Forging Press
Post-Forging Treatment
The conventional treatment method is to bury the forged 1.2714 steel in the sand pit for heat preservation, the purpose is to let the material cool down slowly to prevent cracks.
But for 1.2714 steel that is sensitive to white spots, in order to prevent white spots from being produced during the cooling process, dehydrogenation heat treatment should be done in time to allow the hydrogen inside the material to fully diffuse and escape.
1.2714/56NiCrMoV7-THE COMPREHENSIVE FAQ GUIDE
DIN 1.2714/56NiCrMoV7,as Chromium-nickel-molybdenum-vanadium alloy hot work die steel, is known for stable performance.As a special steel grade in hot work die steel, we certainly want to learn more about this particular kind of steel to properly figure more out about it.
Reading our guide,we will guide you to a better and deeper understanding of what 1.2714 steel is, so as to help you choose 2714 steel from a more comprehensive perspective.
WHAT IS HOT WORK TOOL STEEL?
Hot work tool steel refers to alloy tool steel suitable for making molds for thermal deformation processing of metals, such as hot forging dies, hot extrusion dies, die-casting dies, and hot upsetting dies.
Since hot working molds work under high temperature and high pressure conditions for a long time。Therefore, mold materials are required to have high strength, hardness and thermal stability,especially should have high thermal strength, thermal fatigue, toughness and wear resistance.

Hot Work Tool Steel Application
The hot work mold bears a great impact when it is working. The mold cavity is in contact with high-temperature metal and repeated heating and cooling cycles. It can be said that its use conditions are extremely harsh. In order to meet the requirements of the hot work die, the hot work tool steel should have the following basic characteristics:
- High high temperature strength and good toughness
- Good wear resistance
- High thermal stability
- Excellent thermal fatigue resistance
- High hardenability
- Good thermal conductivity
- Good forming process performance
General Hot Work Tool Steel Classification
- Low alloy hot work tool steel:55NiCrMoV6/1.2713,56NiCrMoV7/1.2714
- Medium alloy hot work tool steel:AISI H13 Ι 1.2344,AISI H11/1.2343
- Tungsten hot work tool steel:AISI H21,AISI H22.
QUICK QUESTIONS FOR 1.2714 STEEL
What Is The Hardness For 1.2714 Steel?
Normally, 1.2714 hot work tool steel is used in heat treatment condition.High hardness will be obtained after quenching and tempering.
1.2714 steel will generally be pre-hardened to hardness range of 38-53HRC
The application of specific hardness is roughly as follows:
- Normal use condition,Hardness 46~50HRC
- Small-part extrusion die with heat-resistance cracking as the main performance,Hardness 50~53HRC
- Toughness as the main performance,Hardness 43~46HRC
What Is The Tensile Strength of 1.2714 Steel?
After quenching and tempering heat treatment, 1.2714 steel not only obtained high hardness, correspondingly also obtained high strength.
With hardness 380-420HB,The corresponding tensile strength is from 1200 to 1400Mpa.
Can 1.2714 Steel Be Water Quenched?
1.2714 steel can be water quenched, but as alloy tool steel, The rapid cooling rate of water quenching leads to an increase in the internal stress of the material, and an increase in the tendency of deformation and cracking.
As 1.2714 steel with high hardenability, it is more suitable for oil with a slow cooling rate as a quenching medium.
How Is The Hardenability of 1.2714 Steel?
The hardenability of steel mainly depends on its chemical composition, especially containing alloying elements that increase hardenability. The steel with good hardenability can make the whole section of the steel part obtain uniform mechanical properties.
1.2714 steel has such good hardenability.The Cr. Ni. Mo element is added to 1.2714 steel, mainly to improve the hardenability of the steel, especially when working together, the hardenability is significantly improved.
For example, a mold of 300mm x 300mm x 400mm can be thoroughly hardened, and the hardness of the entire section is uniform.
Can 1.2714 steel Be Machined Easily?
It depends on the heat treatment condition when machining 1.2714 steel.With annealed condition,hardness will below 248HB,it is relatively easy to process.
While after quenched and tempered conditin,harness will exceed 380HB,it is difficult to do turning processing on 1.2714 steel.Fortunately, superhard tool materials, such as CBN tools and PCD tools, can be used to solve this situation.
How To Check Internal Defects of 1.2714 Steel?
The most cost-effective way is ultrasonic testing, which has proven its value.White spots and cracks, the most dangerous defects in the 2714 material, can be directly judged by ultrasonic testing. The pores, looseness and non-metallic inclusions in the material can also be tested by ultrasonic to determine whether they exceed the standard.
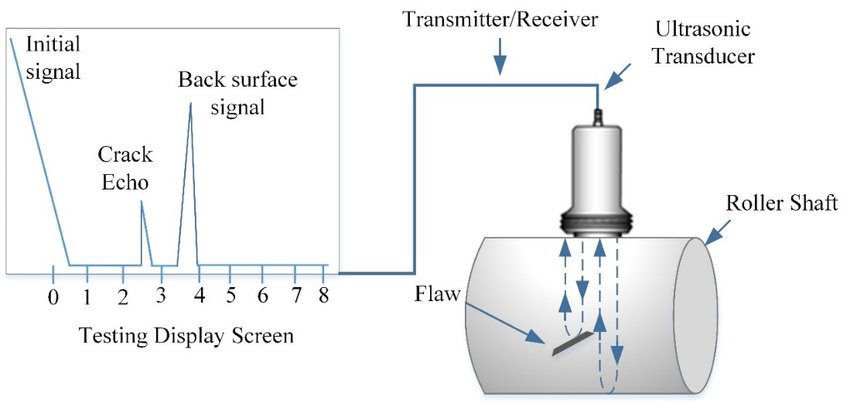
Ultrasonic Testing Principle Diagram
HEAT TREATMENT FOR 1.2714 STEEL
How To Annealing 1.2714 Steel?
Although the annealing time is long and the production efficiency is low, 1.2714 steel needs to be annealed under certain circumstances.
- Stress Relief Annealing
Improve or eliminate various structural defects and residual stress caused by 1.2714 steel during forging,rolling and straightening, and prevent material deformation and cracking.
Generally, the stress relief annealing temperature is controlled at 450-500°C,the temperature of stress relief annealing should generally be 20~30℃ lower than the last tempering temperature, so as not to reduce the hardness and mechanical properties.
- Complete Annealing
Also refers to Recrystallization Annealing.Refine the internal grains of 1.2714 steel, uniform structure to improve its mechanical properties, reduce its surface hardness for machining, and prepare the structure for final heat treatment (quenching & tempering).
The complete annealing temperature of 1.2714 steel is controlled at 760-780°C, and the heating rate usually does not exceed 100°C/hour.The holding time should be determined according to the workpiece shape, size,original structure state, furnace capacity, heating equipment and other factors. Generally, it can be calculated according to the thickness of the workpiece for one hour per 20 mm.
The cooling after annealing should be sufficiently slow, and furnace cooling can be used, and the annealing hardness for 1.2714 steel is below 229HB.
How To Quenching And Tempering 1.2714 Steel?
As a member of hot work tool steel, 1.2714 steel is often used in high temperature and harsh working environment, so its performance requirements are high. This requires us to quench and temper it to meet various performance requirements.
- 1.2714 Steel Quenching
From the consideration of quenching medium, our priority is oil.The cooling effect is slower than that of water, which can prevent quenching cracking and serious deformation.
The quenching temperature of 1.2714 steel should be selected within the temperature range where the austenite grains do not grow, generally controlled between 840-860°C. When heating, it needs to be preheated once or twice to ensure uniform heating.
The selection of the holding time should ensure the completion of the structural transformation and the degree of solid solution of the alloying elements. If the holding time is too short, the thermal hardness and tempering resistance of 1.2714 steel will be reduced.
- 1.2714 Steel Tempering
The tempering of 1.2714 steel should be carried out immediately after quenching.The tempering time should be sufficient, otherwise the hardness of the core of the material will be high, which will easily cause cracking
When cooling after tempering, attention should be paid to prevent the second type of temper brittleness,and at the same time perform secondary tempering. The tempering temperature is about 10°C lower than the first tempering temperature, and the holding time can be shortened by 20%-25%.
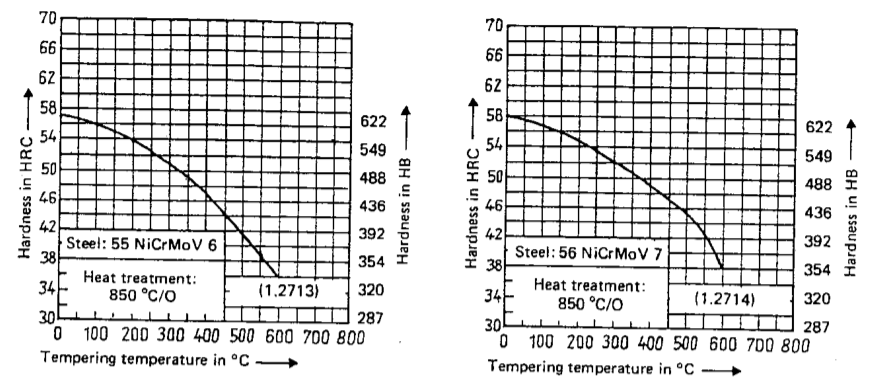
1.2714 Steel Hardness Vs Tempering temperature
| Tempering Temperature,℃ | 400-480 | 500-550 | 570-650 |
| Hardness,HRC | 42-46 | 38-41 | 32-36 |
1.2714 STEEL VS 1.2713 STEEL
Chemical Composition Comparison
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | V |
| 1.2714/56NiCrMoV7 | 0.50-0.60 | 0.1-0.4 | 0.65-0.95 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | 1.0-1.2| 1.50-1.8 | 0.45-0.55 | 0.07-0.12 |
|
| 1.2713/55NiCrMoV6 | 0.50-0.60 | 0.1-0.4 | 0.65-0.95 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | 0.6-0.8| 1.50-1.8 | 0.25-0.35 | 0.07-0.12 |
|
From the above table,we can see the biggest difference lies in the content of Cr and Mo.Due to composition factors, the manufacturing cost of 1.2714 steel is slightly higher than that of 1.2713 steel, but the performance of the two is very close.1.2714 steel can be regarded as an upgraded version of 1.2713 steel.
Heat Treatment Data Comparison In Quenched and Tempered Condition
| Grade | Quenching Temperature,°C | Quench Medium | Tempering Temperature,°C | Hardness after Tempering,HRC |
| 1.2714/56NiCrMoV7 | 830-870 860-900 | Oil Air | See Hardness-Tempering Temperature Curves as below |
|
| 1.2713/55NiCrMoV6 | 830-870 | Oil | ||
Remarks | 1.2714/56NiCrMoV7:Oil Quenching at 850°C,Tempering at 500°C Minimum Hardness Requirement:44HRC |
|||
| 1.2713/55NiCrMoV6:Oil Quenching at 850°C,Tempering at 500°C Minimum Hardness Requirement:40HRC |
||||
Principal Applications Comparison
DIN 1.2713/55NiCrMov6 and DIN 1.2714/56NiCrMoV7 both belong to hot workng tool steel group,you can know from the grade name, they are very close in all aspects,but still a bit different, for example, in the application,they have different focuses.
1.2713 tool steel is mainy used for hammer forging dies for medium and small dimensions,while 1.2714 tool steel focus on hammer forging dies up to the largest dimensions,particularly also with heavy embossing; part dies, die holders, plungers for extrusion presses.
WHERE CAN YOU BUY HIGH-QUALITY 1.2714 STEEL?
When you do everything possible to buy high-quality 1.2714 steel but you are struggling to find a suitable manufacturer, we are here-Fuhong Steel!
We are a manufacturer of the highest quality special steel. We can fully meet your needs for 1.2714 steel, which stems from our rich manufacturing experience and strict quality control system.
What We Supply For DIN 1.2714/56NiCrMoV7 Steel
| Supply Form | Size(mm) | Process | Tolerance | |
Round | Φ6-Φ100 | Cold Drawn | Bright/Black | Best H11 |
Φ16-Φ350 | Hot Rolled | Black | -0/+1mm | |
| Peeled/ground | Best H11 | |||
Φ90-Φ1000 | Hot Forged | Black | -0/+5mm | |
| Rough Turned | -0/+3mm | |||
Flat/Square/Block | Thickness :120-800 | Hot Forged | Black | -0/+8mm |
| Width:120-1500 | Rough Machined | -0/+3mm | ||
Heat Treatment:Annealed(+A),Quenched & Tempered(+QT)
Machining:Turning/Milling/Drilling/Peeling/Polishing