CK45 steel, with an average carbon content of 0.45%, is classified as medium carbon steel, which is one of the most widely used non-alloy carbon steels in German standards.
Similar to American Standard 1045 steel, CK45 steel has good tensile properties and machinability, so it is widely used in the field of machinery manufacturing.
CK45 Steel can be formed by hot rolling and forging, and is generally supplied in an untreated or normalized condition.Through further heat treatment (such as quenching and tempering), the comprehensive properties of C45 steel can be improved.

CK45 STEEL CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
| Standard | Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S |
| SEW550 | CK45/1.1191 | 0.42-0.50 | ≤0.35 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 |
| DIN 17200 | CK45/1.1191 | 0.42-0.50 | ≤0.4 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 |
CK45 STEEL RELATED STANDARD & EQUIVALENT GRADE
CHINA | GB 3077:45#
USA | ASTM A29: 1045
JAPAN | JIS G4051:S45C
Europe | EN10083:C45
UK | BS970:EN8/080M40
What is the Difference Between CK45 and C45E Steel?
CK45 grades come from early German standards, such as SEW550 and DIN17200, while C45E comes from 21st century European standards, such as EN10083 and EN10250. They share the number code 1.1191, so it can be said that C45E replaced CK45, but CK45 is still used now.
| Standard | Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo |
| SEW550 | CK45/1.1191 | 0.42-0.50 | ≤0.35 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | - | - | - |
| DIN 17200 | CK45/1.1191 | 0.42-0.50 | ≤0.04 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | - | - |
| EN10083 | C45E/1.1191 | 0.42-0.50 | ≤0.04 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.4 | ≤0.4 | ≤0.1 |
| EN10250 | C45E/1.1191 | 0.42-0.50 | ≤0.04 | 0.50-0.80 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.4 | ≤0.4 | ≤0.1 |
It can be seen from the above table that both CK45 and C45E are high-quality steels, and they have strict control over the harmful elements of sulfur and phosphorus. In particular, C45E puts forward higher requirements for the control of residual alloy elements Cr, Ni, and Mo.
CK45 STEEL FORGING
- Initial Forging Temperature:1200℃
- Final Forging Temperature:800℃
- Heating Rate:Strictly control the heating speed, which should be uniform and stable to prevent cracking caused by improper heating.
- Forging Ratio:above 4:1
- Post-Forging Treatment:CK45 steel should be slowly cooling after forged.
CK45 STEEL HEAT TREATMENT
Temperature Selection for Different Types of Heat treatment for CK45 Steel
- Soft Annealing:650 – 700°C,Cooling in furnace,hardness below 207 HBW
- Normalizing:840-870°C
- Water Quenching:820-850°C
- Oil Quenching:830-860°C
- Tempering:540-680°C
Jominy Quenching Test Curve For CK45 Steel
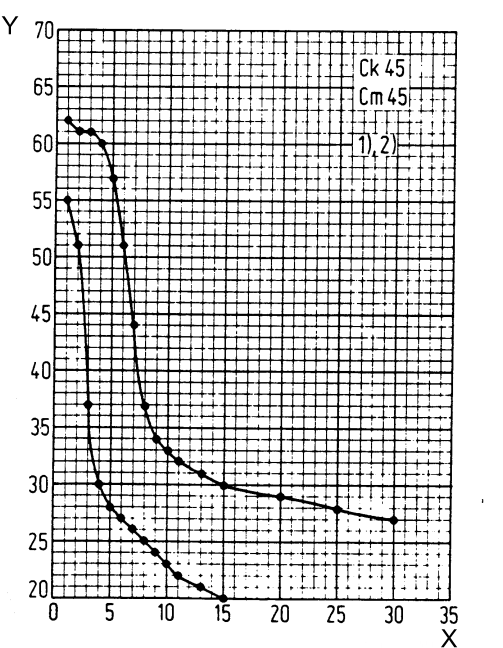
Quenching at 850°C
X:Distance from quenched end,in mm
Y:Hardness,HRC
| Distance from quenched end mm | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
CK45 | HRC Max | 62 | 61 | 61 | 60 | 57 | 51 | 44 | 37 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 |
| HRC Min | 55 | 51 | 37 | 30 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | - | - | - | |
Guideline value Curve for CK45 Steel Mechanical Property
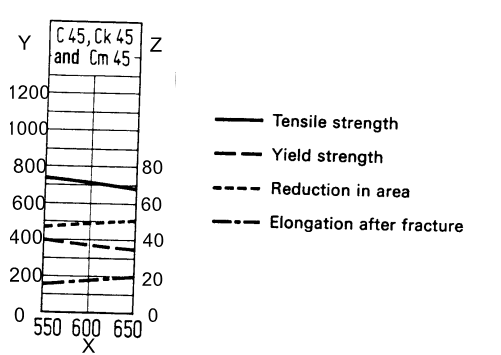
X:Tempering temperature,oC
Y:Tensile and Yield Strength,Mpa
Z:Elongation and Reduction in area,%
CK45 Steel Mechanical Property at 20oC for Forged parts in Normalized condition
| Diameter mm | ≤250 | 250-500 | 500-1000 |
| Tensile Strength Mpa | 590-720 | 590-720 | 590-720 |
| Yield Strength Mpa | ≥325 | ≥305 | ≥295 |
Elongation % | L:≥18 T:≥14 | L:≥16 T:≥13 | L:≥15 T:≥12 |
Impact Charpy J | L:≥31 T:≥24 | L:≥27 T:≥21 | L:≥24 T:≥17 |
C45 STEEL SUPPLY FORM & SIZE & TOLERANCE
Hot Forged Round bar:Φ80-Φ1000mm
Hot Rolled Round bar:Φ16-Φ350mm
Hot Forged Square bar: Max Thickness:500mm
Flat bar/Blcoks:Thickness :120-800mm ,Width:120-1500mm
| Surface Finish | Black-Forged | Black-Rolled | Turned | Grinding | Polished | Peeled | Cold Drawn |
| Tolerance | (0,+5mm) | (0,+1mm) | (0,+3mm) | Best h9 | Best h11 | Best H11 | Best H11 |



