As a high-quality carbon structural steel, C50 steel is defined as a non-alloy steel with an average carbon content of about 0.50% as per European standards.
As a medium carbon steel, C50 steel has high strength and hardness, medium machinability, but low cold deformation plasticity and poor weldability.
C50 steel is usually used after heat treatment such as normalizing or quenching and tempering, or high-frequency surface quenching.It is usually used for parts that require high strength, wear resistance or elasticity, and small dynamic load and impact load, such as forged gears, machine tool spindles, engine spindles, rolls, tie rods, spring washers, etc.

C50 STEEL CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
| Standard | Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni |
| EN10250 | C50/1.0540 | 0.47-0.55 | ≤0.4 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤ 0.4 | ≤ 0.1 | ≤ 0.4 |
| SEW550 | CK50/1.1206 | 0.47-0.55 | ≤0.35 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | - | - | - |
| DIN17200 | CK50/1.1206 | 0.47-0.55 | ≤0.4 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.03 | - | - | - |
C50 STEEL RELATED STANDARD & EQUIVALENT GRADE
China | GB 3077:50
USA | ASTM A29:1050
Japan | JIS G4051:S50C
UK |BS970: EN8/EN9
C50 STEEL PHYSICAL PROPERTY
| Density, g/cm3 | 7.86 |
| Specific heat capacity,(0~100℃),J/(kg.k) | 498 |
| Linear expansion coefficient,10^-6/k | 12.06(0-100℃) |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.29 |
| Elastic Modulus,Mpa | 207407 |
| Shear modulus,Mpa | 81100 |
| Thermal conductivity,W/(m.K) | 47 |
C50 STEEL FORGING
- Initial Forging Temperature:1200℃
- Final Forging Temperature:850℃
- Forging Ratio:above 4:1
- Post-Forging Treatment:C50 steel should be slowly cooling after forged.
C50 STEEL HEAT TREATMENT
Critical Temperature for Heat Treatment of C50 Steel
- Ac1:725℃
- Ac3:760℃
- Ar1:690℃
- Ar3:721℃
Temperature Selection for Conventional Heat treatment for C50 Steel
- Annealing:820 – 840°C,Cooling in furnace,hardness below 187 HBW
- Normalizing:820-870°C,Cooling in air,hardness about 217HBW
- Quenching:810-850°C,Medium:Water\Oil
- Tempering:550-660°C
C50 Steel Mechanical Property with Quenched and Tempered Condition
| Tensile Strength Mpa | Yield Strength Mpa | Elongation % | Reduction of Area % | Impact Charpy-V J |
| ≥630 | ≥375 | ≥14 | ≥40 | ≥31 |
C50 Steel Tempering Temperature Vs Hardness
| Grade | Quenching | Tempering Temperature,ºC | |||||||
| Temperature,ºC | Hardness,HRC | 150ºC | 200ºC | 300ºC | 400ºC | 500ºC | 550ºC | 600ºC | |
| C50 | 830ºC | 58-59 | 58 | 55 | 50 | 41 | 33 | 26 | 22 |
Jominy Quenching Test Curve For C50E Steel
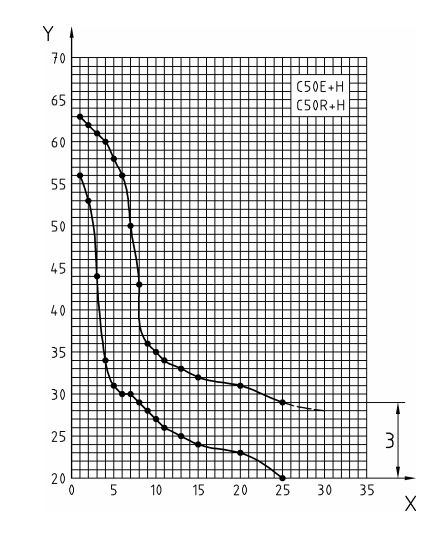
Quenching at 850°C
X:Distance from quenched end,in mm
Y:Hardness,HRC
3: H level
| HRC-mm | Type | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| MIN | +H | 56 | 53 | 44 | 34 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 20 | - |
| MAX | 63 | 62 | 61 | 60 | 58 | 55 | 50 | 43 | 36 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 31 | 29 | 28 |
Guideline value Curve for C50 Steel Mechanical Property
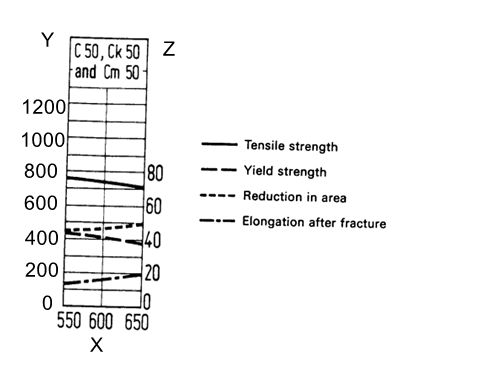
X:Tempering temperature,oC
Y:Tensile and Yield Strength,Mpa
Z:Elongation and Reduction in area,%
WHAT WE SUPPLY FOR C50 STEEL
Hot Forged Round bar:Φ80-Φ1000mm
Hot Rolled Round bar:Φ16-Φ350mm
Hot Forged Square bar: Max Thickness:500mm
Flat bar/Blcoks:Thickness :120-800mm ,Width:120-1500mm
| Surface Finish | Black-Forged | Black-Rolled | Rough Turned | Cold Drawn | Peeled | Polished | Grinded |
| Tolerance | 0/+5mm | 0/+1mm | 0/+3mm | Best H11 | Best H9 | Best H9 | Best h8 |
















